About


The
NMTrypI concept is based on the development of
innovative drug leads by using a common drug discovery platform to study the mechanism-based
combinations of known and investigational drugs and dual-target inhibition. The platform is established
by experts in their respective fields from Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) and the public research
sector in Europe and disease-endemic countries.
The innovative concept is reinforced by the identification of preclinical
biomarkers enabling the proteomic profiling of the compound to understand the mechanism
of action (MoA biomarkers) and to detect the efficacy of the lead
candidate (pharmacodynamic biomarkers).
The new NMTrypI platform will perform the screening of compound libraries, lead development, testing
in mice, hamsters and dogs as a reservoir for the visceral leishmaniasis disease as well as
toxicology and
safety testing (in vitro against different
cell types and in vivo in animals) to overcome current
limitations in anti-trypanosomatid therapy.
The major strength of the Consortium lies in the complementary expertise of the partners and the integrated platform that will provide:
EXPECTED IMPACT RELATED TO THE WORK PROGRAMME
The application of the new NMTrypI approach is expected to lead to an adapted and affordable treatment
of Trypanosomatidic Infections in disease-endemic countries. The NMTrypI project may contribute to
a breakthrough in finding a suitable therapy for Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs).
Carrying out the project at an international level with the inclusion of EU and disease-endemic countries
in the consortium provides a unique blend of experts to work in the field of Trypanosomatidae research which
further increases the versatility of the project's outcome.
The research SMEs involved in the project aim at exploiting the results generated
to create more revenues for the companies and therefore strengthen their competitiveness, allowing them to further
develop their research and also to create more jobs.
ETHICAL ASPECTS OF THE NMTrypI PROJECT
The aim of the NMTrypI project is the discovery of potentially useful drugs for trypanosomatid diseases
affecting humans and dogs for which no satisfactory treatment exists.
The research project involves the use of experimental animals, namely mice, hamsters and dogs. The experimental
approach includes the use of in vitro primary screening to
reduce the need for animal experimentation or at least the number of animals needed.
However, the in vitro selection of hits and leads does not preclude the employment of limited
numbers of animals as the final step of evaluation for the new treatments. Nonetheless, the selection
model employed has drastically reduced the need for experimental animals.
European regulation and international codes of conduct
The use of animals in NMTrypI research activities will take into account and strictly adhere to:
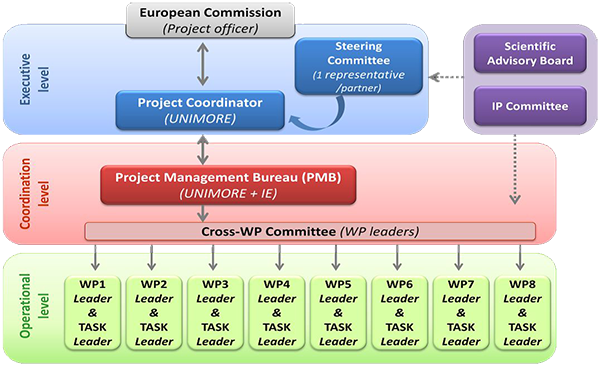
SCIENTIFIC ADVISORY BOARD
The
Scientific Advisory Board (SAB) assists and facilitates the decisions made
by the Steering Committee and provides scientific advice to the project.
The
SAB is composed of four external key scientists:
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY (IP) COMMITTEE
The IP Committee is composed of one IP expert from UNIMORE
(M. P. Costi), one from an SME (A. Venturelli, TYDOCK), and one from an academic institution (T. Calogeropoulou,
NHRF).
The IP Committee is a consulting body to the project and consortium in IP topics and has three main functions:
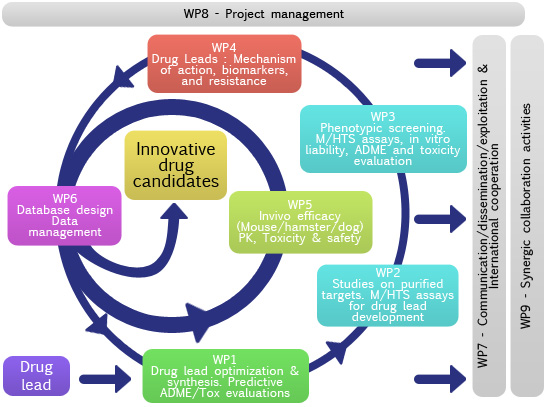
WP1: Lead optimization & synthesis. Predictive
ADME-Tox evaluation.
The overall objective of WP1 is to generate lead compounds belonging to three compound classes:
i) Synthetic folate pathway-targeting pteridine, benzothiazole and thiadiazole derivatives.
ii) Improved miltefosine analogs.
iii) Natural products.
WP1 leader: Dr. Theodora Calogeropoulou, NHRF
Main outcomes of WP1:
WP2: Studies on purified targets. M/HTS assays for
lead development.
WP2 integrates the screening of compound libraries. The target proteins will be obtained
and inhibitor-target interaction studies will be performed using biophysical methods (X-ray
crystallography, fluorescence spectroscopy, isothermal titration calorimetry).
The optimized leads will be identified through target testing in high-throughput screening (HTS), and combinations will be
prioritized according to cellular liability assay results. In vitro
toxicity, ADME and safety (in WP3) are prepared for delivery in animals (WP5).
WP2 leader: Prof. Dr. Maria Paola Costi, UNIMORE
Main outcomes of WP2:
WP3: Phenotypic screening. M/HTS assays,
ADME-Tox evaluation.
WP3 concerns the development of functional screening through cellular testing.
Natural compound mixtures are first tested on sensitive parasites and optimal mixtures are next
re-tested against relevant drug-resistant strains. Only the selected mixtures from the dereplication
process will be purified, and active compounds isolated and characterized. Final ranking and selection
of the leads identified with related molecular and biological properties will be done
based on Target Drug Lead Profile (TDLP) criteria.
Decisions on compound progression to WP5 for animal testing or WP1 for further chemical modification will be taken.
WP3 leader: Dr. Sheraz Gul, Fraunhofer IME-SP
Main outcomes of WP3:
WP4: Drug leads:
mechanism of action,
biomarkers, and resistance.
The aims of WP4 are to identify the mechanism of action and off-target effects for improving the
design of optimized leads and to identify potential drug resistance that may evolve from the delivery of
the leads to the parasites in vitro.
The off-target information identified will be fed back into lead
optimization in WP1. Combinations of two folate pathway proteins (pteridine reductase 1,
PTR1 and dihydrofolate reductase, DHFR) inhibitors will be studied independently
and then together, following the appropriate protocols.
Biomarkers of drug lead action on parasites will be obtained through a proteomic
approach.
The evaluation of the efficacy of drug candidates in T. cruzi (Chagas disease), T. brucei
(sleeping sickness), L. major, L. infantum and L. donovani (leishmaniases) infections in
animals will be performed in WP5.
WP4 leader: Dr. Joachim Clos, BNI
Main outcomes of WP4:
WP5: Evaluation of animal models of candidate drugs. Pharmacokinetic,
toxicity and safety studies.
WP5 aims at determining the efficacy of non-toxic and safe selected leads
(from WP2) against laboratory models of trypanosomatid infections (Trypanosoma spp, Leishmania spp).
Secondly, WP5 aims at evaluating the in vivo
toxicity, safety, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic
parameters of selected drugs in different organs of the mice & hamster models.
Thirdly, WP5 aims at testing specificity and leishmanicidal activity in dog models for the
most promising candidate drugs.
WP5 leader: Dr. Anabela Cordeiro-da-Silva, IBMC
Main outcomes of WP5:
WP6: Database design and data management.
The main objective of WP6 is to provide comprehensive data management for the project, i.e.
a place to collect, structure and share data: experimental data, models, standard operating
procedures (SOPs), as well as a participant directory.
WP6 leader: Dr. Wolfgang Müller, HITS
Main outcomes of WP6:
WP7: Communication/Dissemination/Exploitation & International cooperation.
The main objectives of WP7 are the following: